Relic Quest: In Search Of Relic First Descendant Secrets Unveiled
In search of relic first descendant: Unraveling the Enigmatic Past
Have you ever wondered about the silent stories held within ancient objects? The phrase "in search of relic first descendant" embodies this allure, encapsulating the captivating quest to uncover the origins and lineage of a revered artifact or object, often shrouded in mystery and historical significance. This is not merely about finding old things; it's about unlocking the secrets of civilizations. This pursuit involves meticulous research, exploration, and the unraveling of intricate connections to trace the provenance of a relic, leading to a deeper understanding of its cultural, historical, and spiritual value. It is a detective story that spans centuries.
The importance of such endeavors lies in preserving our collective heritage, connecting us to the past, and shedding light on the evolution of civilizations. By embarking on these quests, we gain insights into the lives, beliefs, and craftsmanship of our ancestors, fostering a sense of continuity and appreciation for the tangible remnants of our shared history. Its about understanding who we are by understanding where we came from, a journey charted by the relics left behind.
- Discover Who Is The Most Successful Shark Tank Investor Mr Wonderful
- Why Charley Crockett Without A Hat Unveiling The Artists Soul
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| The Term | "In Search of Relic First Descendant" - Represents the pursuit of origins and lineage of ancient objects. |
| Significance | Preserves heritage, connects to the past, illuminates civilization's evolution. Provides insights into lives, beliefs, and craftsmanship of ancestors. |
| Pursuit | Involves meticulous research, exploration, and unraveling of connections to trace an object's provenance. |
| Goal | Deepen understanding of cultural, historical, and spiritual value of relics. |
| Importance | Fosters continuity and appreciation for tangible remnants of shared history. |
in search of relic first descendant
The pursuit of relics and the study of their first descendants offer invaluable glimpses into the past, illuminating cultural practices, technological advancements, and societal structures. It is an interdisciplinary endeavor, requiring the skills of historians, archaeologists, scientists, and even linguists to fully appreciate the story behind an artifact.Key Aspects
- Historical Significance: Uncovering the origins and lineage of relics provides insights into key historical events, and cultural practices. It's a way to touch the past, to see through the eyes of those who came before.
- Cultural Heritage: Relics serve as tangible links to our cultural past, representing the beliefs, values, and traditions of our ancestors. These are not just objects, but embodiments of a culture's soul.
- Scientific Research: Relics offer opportunities for scientific analysis, shedding light on ancient materials, techniques, and the environment of the past. Science provides the tools to unlock the physical secrets these objects hold.
Explore the connection between "Historical Significance" and "in search of relic first descendant"
- Historical relics provide tangible evidence of past events, offering insights into political, social, and cultural dynamics. They are the witnesses to history, silent but eloquent.
- The study of first descendants can reveal the role of individuals in shaping historical narratives and preserving cultural traditions. It's about understanding the human element, the individuals who influenced the course of events.
- By connecting relics to specific historical figures or events, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the context and significance of these objects. Its about weaving together the object, the person, and the moment in time.
{point}
The identification of first descendants is crucial in unraveling the lineage and authenticity of relics. It adds a human dimension to the pursuit, connecting the artifact to a specific line of people.Facets
- Genealogical Research: Tracing the lineage of relics through historical records, such as birth, marriage, and death certificates. This is the meticulous work of building a family tree for an object.
- DNA Analysis: Utilizing DNA testing to establish genetic connections between relics and potential descendants. Science provides the definitive link, proving or disproving the connection between object and person.
- Oral Traditions: Examining passed-down stories and legends within families or communities that may hold clues to the provenance of relics. These are the whispers of history, sometimes distorted but often containing kernels of truth.
| Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Genealogical Research | Provides documented evidence of lineage | Relies on the availability and accuracy of historical records |
| DNA Analysis | Establishes genetic connections | Requires access to DNA samples and can be expensive |
| Oral Traditions | Preserves cultural knowledge | Can be subject to distortion or misinterpretation over time |
in search of relic first descendant
The quest to uncover the origins and lineage of relics, often referred to as "in search of relic first descendant," involves meticulous research, exploration, and the unraveling of intricate connections. It's a complex puzzle with pieces scattered across time and geography. This pursuit encompasses various dimensions, including:
- Historical Significance
- Cultural Heritage
- Scientific Research
- Genealogical Investigation
- DNA Analysis
- Oral Traditions
- Archaeological Discovery
These aspects are interconnected and contribute to the broader understanding of relics and their significance. It's a holistic approach, recognizing that no single method can provide a complete picture. Historical significance provides context for the relic's creation and use, while cultural heritage explores its connection to specific traditions and beliefs. Scientific research offers insights into the materials and techniques employed, and genealogical investigation traces the relic's lineage through historical records. DNA analysis and oral traditions provide additional layers of evidence, while archaeological discovery often leads to the initial identification of relics.
Uncovering the historical significance of relics is a crucial aspect of "in search of relic first descendant." Relics serve as tangible links to the past, offering insights into key historical events, cultural practices, and societal structures during the time of their creation or use. It's like holding a piece of history in your hand. By studying relics and tracing their origins, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the context in which they were created and the role they played in shaping history. The artifacts speak to us if only we know how to listen.- Historical Events: Relics can provide physical evidence of significant historical events, offering tangible proof of their occurrence and details about how they unfolded. For example, the discovery of a relic from a specific battle site can shed light on the strategies, weapons, and tactics used during that conflict. It can transport you back to the battlefield.
- Cultural Practices: Relics can offer insights into the cultural practices and beliefs of past societies. For instance, a relic associated with a particular religious ritual can provide information about the ceremonies, rituals, and spiritual beliefs of that culture. It's a window into the soul of a civilization.
- Societal Structures: Relics can reveal information about the social structures and hierarchies of past societies. For example, a relic associated with a royal family can provide insights into the political and economic systems of that time. It can tell us about power and privilege, about who ruled and who served.
- Technological Advancements: Relics can showcase the technological advancements and craftsmanship of past civilizations. For example, a relic that is a piece of machinery or a tool can provide information about the level of engineering and manufacturing skills possessed by that society. It demonstrates ingenuity and innovation.
- Historical Legacy: Relics embody the historical legacy of a culture, preserving evidence of past events, practices, and achievements. They serve as reminders of the struggles, triumphs, and contributions of previous generations, fostering a sense of continuity and connection to the past. They serve as a reminder of our shared humanity.
- Cultural Identity: Relics play a vital role in shaping cultural identity, providing a sense of belonging and shared heritage. They represent the collective memory and experiences of a people, reinforcing their distinct traditions, beliefs, and values. They are the touchstones of who we are.
- Artistic Heritage: Relics showcase the artistic heritage of a culture, showcasing the skills, techniques, and aesthetics of past artisans. They encompass a wide range of artistic expressions, from sculptures and paintings to ceramics and textiles, reflecting the creativity and imagination of their creators. They embody the beauty and skill of past artisans.
- Religious Significance: Many relics hold deep religious significance, serving as objects of veneration and devotion. They represent the sacred beliefs and practices of a culture, providing a tangible connection to the divine or supernatural. They represent faith and spirituality.
One of the primary ways in which scientific research contributes to the study of relics is through the use of advanced analytical techniques. These techniques, such as radiocarbon dating, material analysis, and DNA testing, allow researchers to determine the age, composition, and provenance of relics with greater precision. This information is essential for establishing the authenticity of relics and placing them within their proper historical context. Science is the ultimate truth-seeker.
- Everything To Know About Michael C Hall Tv Shows A Detailed Guide
- Connor Mccaffrey The Untold Truth Behind This Talented Star
Furthermore, scientific research helps uncover the stories behind relics by examining their physical characteristics and the materials used in their creation. For example, the analysis of pigments and brushstrokes in a painting can provide insights into the artist's techniques and the period in which the artwork was created. Similarly, the examination of metalwork or ceramics can reveal the technological advancements and craftsmanship of past civilizations. Science brings the past to life.
The practical significance of scientific research in the study of relics is immense. It enables researchers to verify the authenticity of relics, determine their age and origin, and gain insights into the historical and cultural context in which they were created. This knowledge contributes to a deeper understanding of our past and helps us appreciate the artistic, technological, and cultural achievements of our ancestors. Every analysis reveals a new detail.
Scientific research is an indispensable component of "in search of relic first descendant." It provides the tools and methods necessary to authenticate, analyze, and interpret relics, unlocking their secrets and enriching our understanding of history and culture. Through science, we can truly understand the past.Genealogical investigation plays a crucial role in "in search of relic first descendant" by establishing the lineage and provenance of relics through the meticulous examination of historical records, family trees, and genetic data. It's like building a family tree for an object, tracing its journey through time. This in-depth research provides invaluable insights into the origins and ownership history of relics, enhancing our understanding of their significance and authenticity. Every record, every connection, reveals a new chapter in the relic's story.One of the primary objectives of genealogical investigation is to trace the lineage of a relic's current possessor back to its original creator or owner. By examining birth, marriage, and death records, as well as other historical documents, researchers can construct a detailed family tree that links the relic to specific individuals and families over time. This information is essential for establishing the authenticity of relics and verifying their connection to historical events or figures. Proving that the object isn't a forgery, and is connected to someone real.
Furthermore, genealogical investigation can uncover fascinating stories about the individuals who owned and cherished relics throughout history. By delving into family archives and personal letters, researchers can shed light on the motivations, beliefs, and cultural practices of relic owners. This knowledge enriches our understanding of the relic's journey and the impact it had on the lives of those who possessed it. Every story of the person that owned it, is also a part of this object.
Genealogical investigation is an indispensable component of "in search of relic first descendant." It provides a systematic approach to tracing the lineage and provenance of relics, unlocking their secrets and enhancing our appreciation for their historical and cultural significance. Through careful study we understand the relic in a much bigger context.DNA analysis plays a significant role in "in search of relic first descendant" by providing a powerful tool to establish genetic connections between individuals and relics, unlocking valuable insights into their provenance and authenticity. Science once again allows us to verify the provenance and lineage.- Identification of Descendants: DNA analysis can be used to identify direct descendants of individuals associated with relics. By comparing the DNA of potential descendants to the DNA extracted from the relic, researchers can establish genetic links and verify the authenticity of the relic's connection to a specific historical figure or family. It can prove who are the right owner of it.
- Lineage Verification: DNA analysis can trace the lineage of relics through multiple generations. By analyzing the DNA of different individuals who have owned or inherited the relic over time, researchers can construct a genetic lineage that provides valuable information about the relic's history and provenance. Helps us to trace to who the object was originally.
- Genetic Provenance: DNA analysis can determine the geographic origin of a relic by comparing its DNA to genetic databases of populations from different regions. This information can provide insights into the cultural context in which the relic was created and the possible routes of its dispersal over time. Helps in understanding where the object was from and why and how it ended up where it is.
- Authentication of Relics: DNA analysis can help authenticate relics by comparing the DNA extracted from the relic to known genetic profiles of individuals associated with it. This comparison can confirm or refute the authenticity of the relic and its connection to specific historical events or figures. Helps us to know is this the real object or just fake.
One of the primary ways in which oral traditions contribute to the search for and understanding of relics is by providing information about their cultural context and usage. Through stories and legends, communities pass down knowledge about the rituals, ceremonies, and beliefs associated with specific relics. This information can help researchers interpret the relic's purpose and significance within a particular cultural or historical framework. We can finally understand the story behind the object and what is the role of it for people.
Furthermore, oral traditions can provide clues to the provenance and lineage of relics. Family histories and genealogies preserved through oral accounts can help trace the relic's ownership and usage over time, linking it to specific individuals or families. This information is crucial for establishing the authenticity of relics and understanding their journey through history. Through the stories, we can trace the history and journey of that object.
Oral traditions are an invaluable component of "in search of relic first descendant." They provide a rich source of information about the cultural context, usage, and provenance of relics, complementing and enriching the understanding gained from written records and scientific analysis. The stories are an important part of the relics and without that we can't understand what is the role of it and what it meant for people.Archaeological discovery plays a crucial role in "in search of relic first descendant" by providing tangible evidence of past civilizations, cultures, and historical events. Through the excavation and analysis of ancient sites, artifacts, and ecofacts, archaeologists uncover relics that shed light on the origins, beliefs, and achievements of our ancestors. Without the hard work of the Archaeologists, there is no object.One of the primary ways in which archaeological discovery contributes to the search for and understanding of relics is by providing physical evidence to support historical narratives and legends. By excavating sites associated with specific historical events or figures, archaeologists can uncover relics that corroborate or challenge existing accounts. For example, the discovery of Tutankhamun's tomb in 1922 provided a wealth of artifacts that illuminated the life and reign of this ancient Egyptian pharaoh. We can finally see the whole image through the work of Archaeologists.
Furthermore, archaeological discoveries can provide insights into the cultural context and usage of relics. By examining the context in which relics are found, such as in temples, burials, or settlements, archaeologists can infer their purpose and significance within a particular society. For instance, the discovery of ritual objects in ancient religious sites sheds light on the spiritual beliefs and practices of past cultures. We can see what the relic means for people and the community.
Archaeological discovery is an indispensable component of "in search of relic first descendant." It provides tangible evidence to support historical narratives, illuminates the cultural context and usage of relics, and contributes to a deeper understanding of past civilizations and their achievements. The work of the Archaeologists is very important because they provide the actual object for us to learn more.This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the topic of "in search of relic first descendant," providing concise and informative answers. Question 1: What is the significance of relics in understanding history and culture?Answer: Relics serve as tangible links to the past, offering valuable insights into the beliefs, practices, and achievements of past civilizations. They provide physical evidence to support historical narratives, illuminate cultural contexts, and contribute to a deeper understanding of our shared heritage.
Question 2: How do modern scientific techniques contribute to the study of relics?Answer: Advanced analytical techniques, such as radiocarbon dating, material analysis, and DNA testing, play a crucial role in authenticating relics, determining their age and origin, and uncovering the stories behind their creation and usage. These scientific methods enhance our understanding of relics and their historical significance.
The study of relics involves a multifaceted approach that combines historical research, scientific analysis, and cultural interpretation. By uncovering the origins, lineage, and significance of relics, we gain insights into the lives, beliefs, and achievements of our ancestors, enriching our understanding of human history and cultural diversity.- Marlon Jacksons Date Of Birth All About The Icons Life
- Axl Roses Kids Does Axl Rose Have Kids Family Life
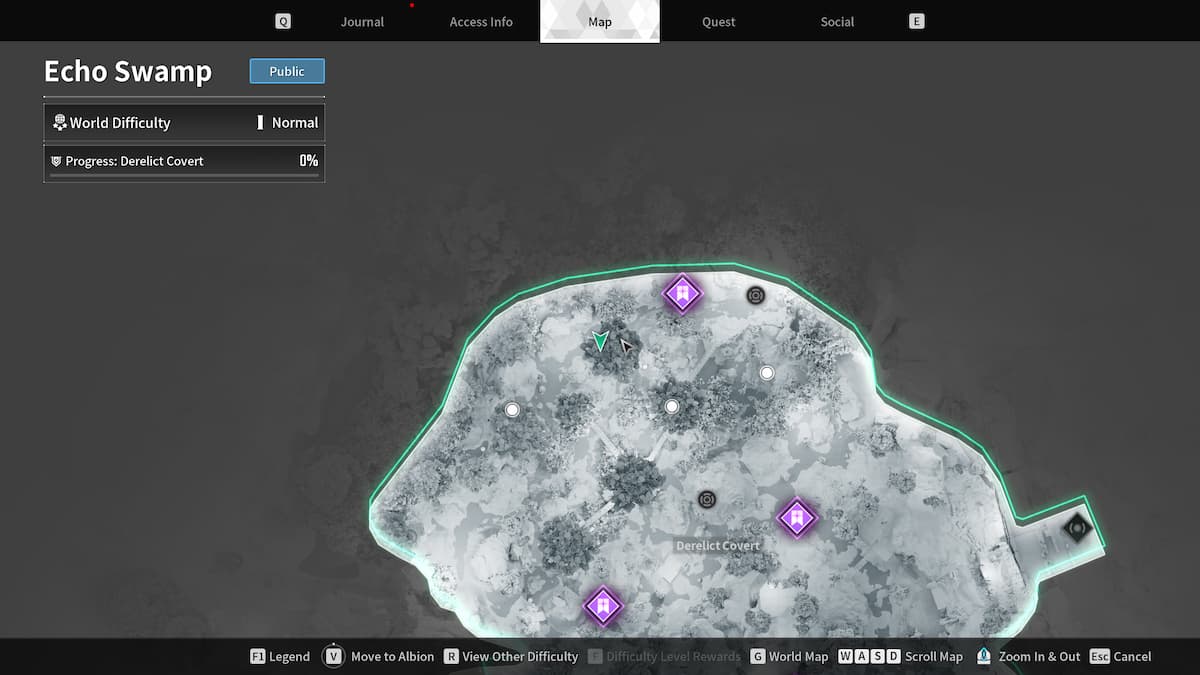
How to Complete In Search of the Relic in The First Descendant
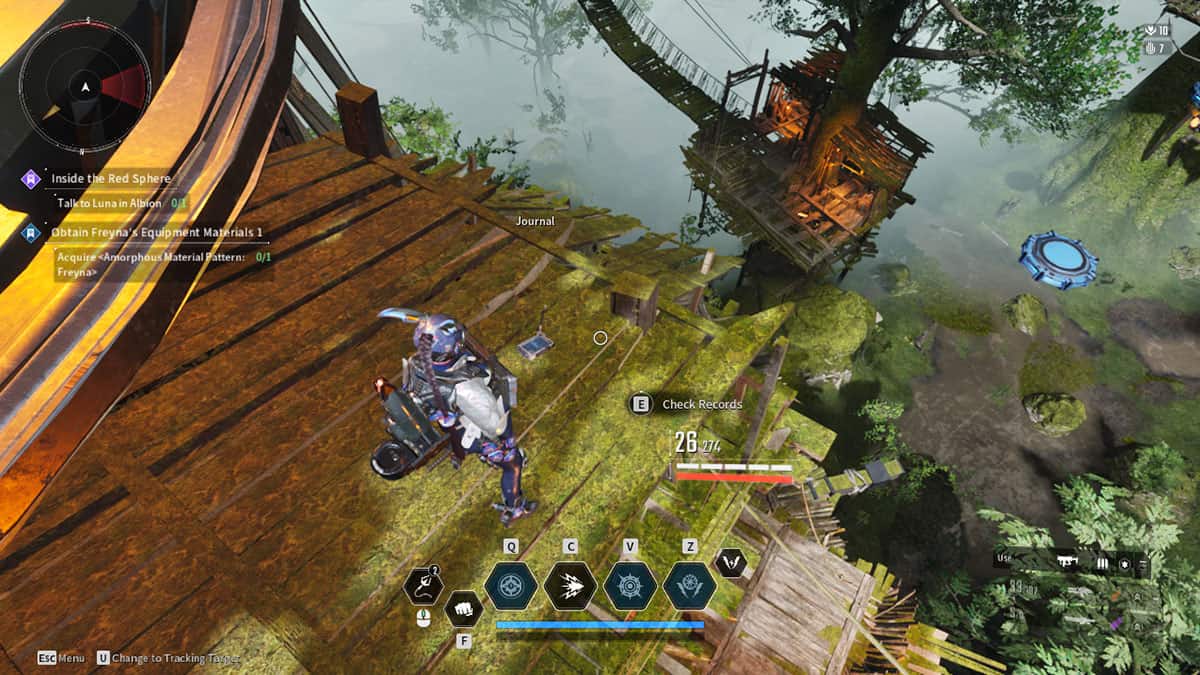
The First Descendant In Search of the Relic Bunny Questline Guide
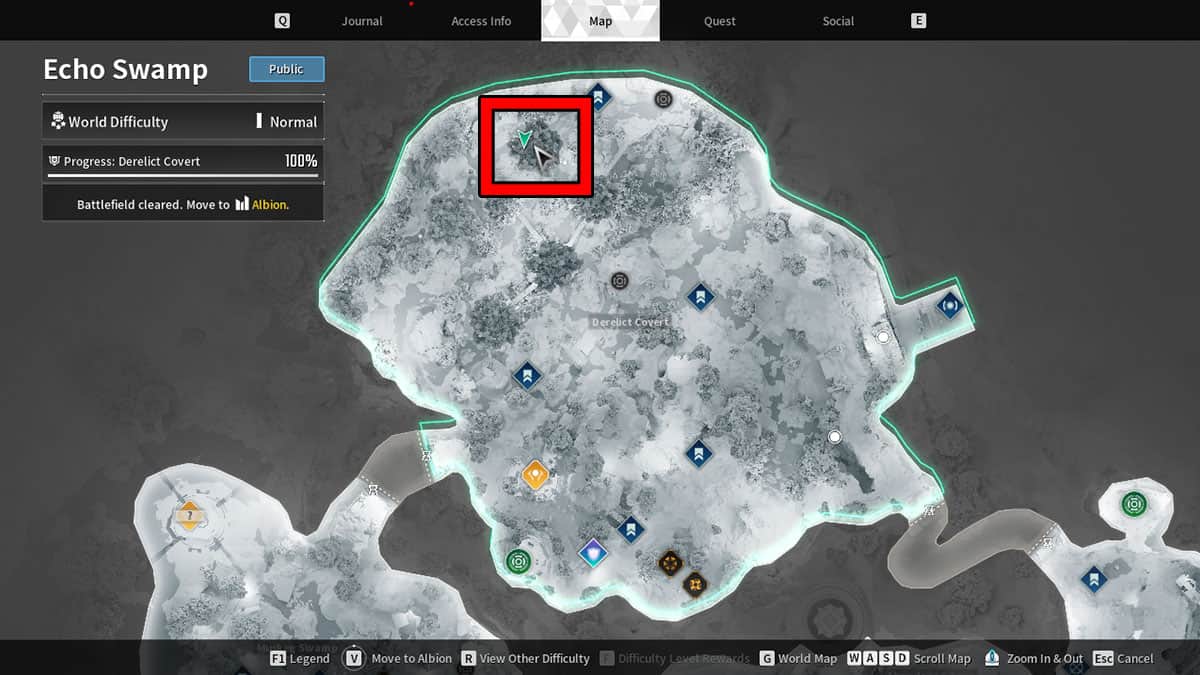
The First Descendant In Search of the Relic Bunny Questline Guide